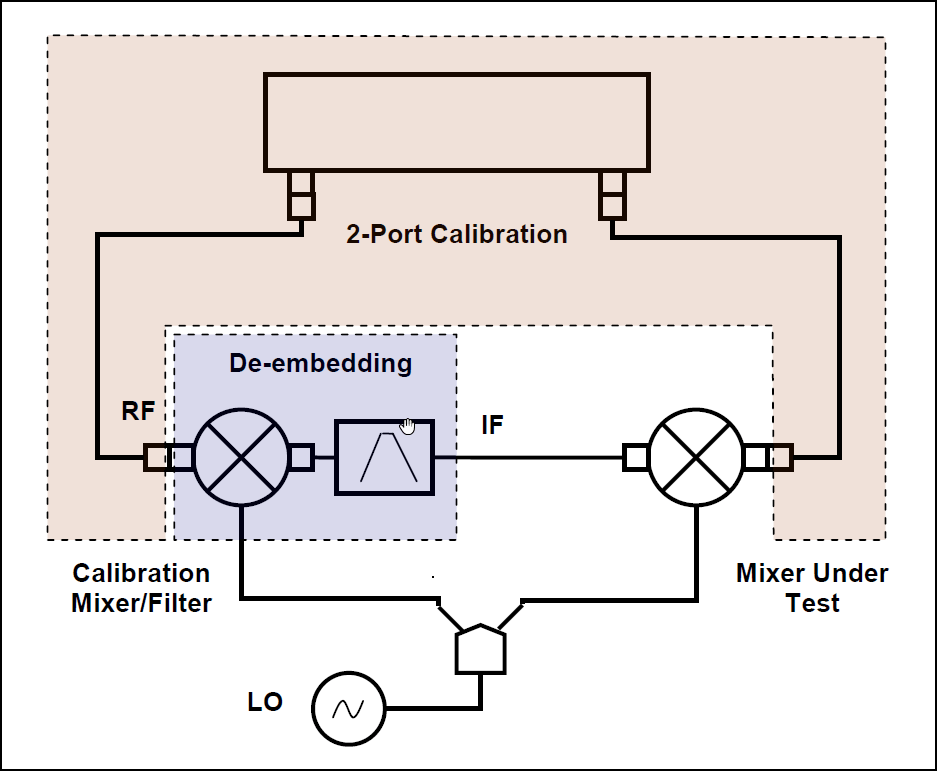
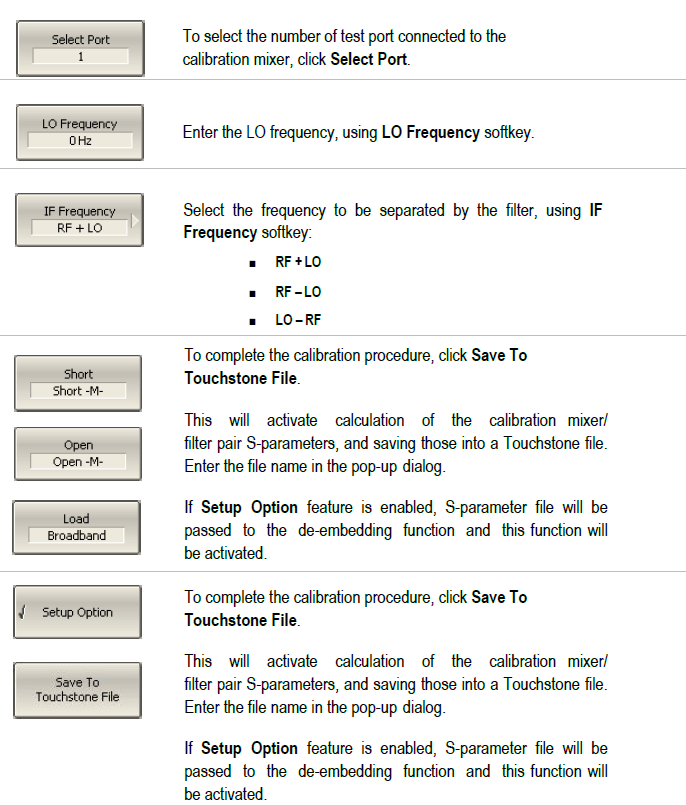
Vector Mixer Measurements
April 13, 2020Introduction
As the demand for high frequency applications increases, RF components such as mixers and filters play a critical role in most RF system design. The vector mixer calibration method allows for measurement of mixer transmission complex S-parameters including phase and group delay of the transmission coefficient. The vector mixer calibration method ensures a matching frequency at both test ports of the analyzer, in normal operation mode. The vector mixer calibration procedure will be outlined in this app note.
Vector Mixer Calibration
The vector mixer measurements require an additional mixer with filter, which is called calibration mixer. The filter separates the IF, which is the input frequency for the mixer under test:
RF + LO
RF – LO
LO – RF
Both calibration mixer and mixer under test are powered from one LO.
The vector mixer measurement is a combination of a 2-port calibration and a de-embedding function (See Figure 1).
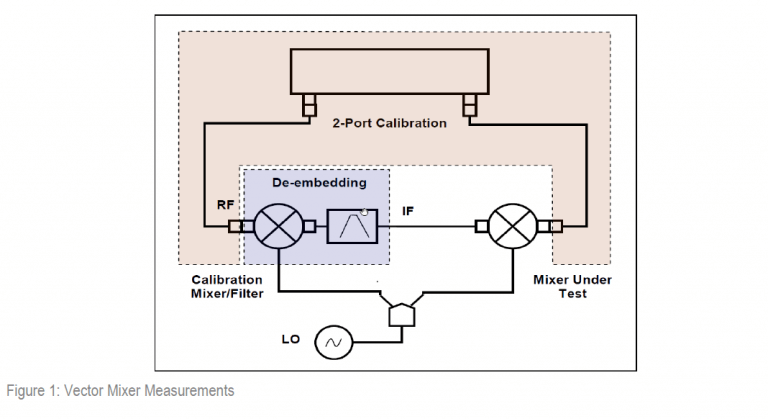
The de-embedding function requires an S-parameter file of the circuit. Acquisition of such a file for the calibration mixer/filter pair is called vector mixer calibration.
To obtain an S-parameter file of the calibration mixer/filter, you need to use SHORT, OPEN, and LOAD calibration standards (See Figure 2).
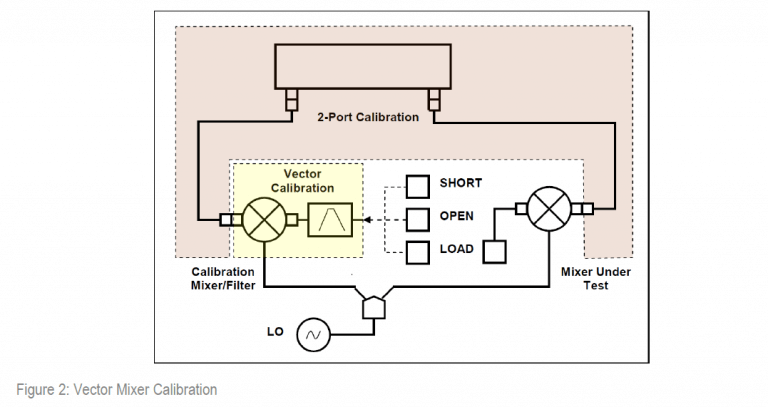
Before you start the calibration, perform the following settings: activate a channel and set its parameters (frequency span, IF bandwidth, etc.), and define the calibration kit.
Perform 2-port
Assemble vector calibration
Set frequency and power of the external LO.

Conclusion
Mixers are an important component in the design of RF receivers and transmitters. To get the most out of the design it is important to carefully measure the operating characteristics of the device. This app note should help you get started with your vector mixer measurements. If you need further clarification on this application note or any assistance with your application, please contact: [email protected].
Related Post
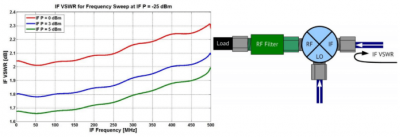
RF Mixer Characterization
April 19, 2018
Mixers are 3-port devices that incorporate nonlinear elements, typically diodes or transistors, to produce the sum or difference of two input frequencies. For example, in transceivers mixers are used to translate radio frequencies (RF) to intermediate frequencies (IF) to allow easier, cheaper, and more accurate processing as well as to translate intermediate frequencies to RF for communication, especially over antennas which are more efficient and smaller at higher frequencies. Engineers developing mixers or integrating mixers in systems often need to measure mixer performance, including conversion loss, phase and group delay, the 1 dB compression point, isolation between ports, and port VSWR. Measurements characterizing these parameters are easily performed on Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) with advanced calibration techniques, including Scalar Mixer Calibration (SMC) and Vector Mixer Calibration (VMC). Both of these calibration methods are described in detail in the operating manuals of Copper Mountain Technologies’ S2 family of VNAs, available for download at www.coppermountaintech.com. This application note will give a brief overview of mixer fundamentals, describe important mixer characteristics, and detail various measurement processes.

Calibration Types and Considerations
April 19, 2018
One of the most frequently asked questions we receive at Copper Mountain Technologies’ sales and support departments goes something like this: “What about calibration?” It’s an unfortunate reality that in the English language, Calibration has two completely distinct definitions. The first relates to checking out the instrument periodically to make sure it is operating within its specifications. “Performance test” is the procedure by which the analyzer performance is verified, typically annually. The second meaning is to do with Measurement or User calibration, a collection of techniques by which measurement accuracy is maximized and made to exclude elements of the system from those measurements (such as cables, adapters and the like). In this application note, we discuss both meanings of calibration as related to Copper Mountain Technologies’ Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs). First, we describe Annual Calibration and then later we discuss measurement calibration.
What Makes a Good VNA?
February 14, 2018
Everyone knows that a good VNA should have both excellent hardware performance and an easy to use software interface with useful post-processing capabilities. There are numerous VNAs in the market with different performance levels; some of them are economy grade, and others are truly laboratory test grade. What separates the two?
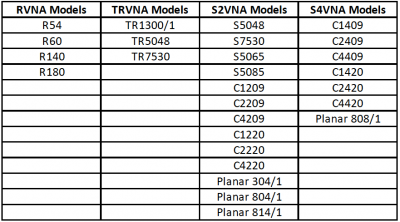
A Guide to CMT VNA Software Families and VNA Series
February 14, 2018
Copper Mountain Technologies (CMT) provides a variety of Vector Network Analyzers (VNA) to accommodate a wide range of test and measurement needs. The CMT VNA family covers a wide span of frequencies starting from 20 kHz, and extending to 20 GHz, with 1-port, 2-port or 4-port configurations. 2-port VNAs are further divided into two groups: one capable of measuring 2-port 1-path measurements, and the other capable of full 2-port 2-path measurements.


Comments (31)